We all use recycled water for drinking and bathing. The water we flush down the toilet is converted into drinking water, and it is the job of sewage treatment plants to make that water fit for human consumption or discharge into rivers and oceans.
Wastewater from sinks, bathrooms, washing machines, toilets and other appliances has to go somewhere. After traveling through miles of sewer networks, it eventually reaches sewage treatment plants, which are tasked with treating and discharging it. Without adequate treatment, sewage will seep into the environment and pollute the ecosystem.
Stp Water
What is sewage?
Sewage is water that has been used with a variety of wastes, pollutants, and impurities, and usually refers to wastewater generated by residential, industrial, commercial, and agricultural activities. Sewage may contain a variety of organic and inorganic substances, including wastewater, chemicals, microorganisms, particulate matter and dissolved matter, the composition of which may vary from source to source.
What is Stp?
STP stands for Sewage Treatment Plant, which is a facility used to treat wastewater generated in urban and industrial areas.The main goal of an STP is to remove hazardous substances and pollutants from the wastewater to ensure that the treated water can be safely discharged into the environment or used for purposes such as irrigation or industrial water.

What types of wastes are contained in sewage?
Sewage contains many types of wastes that can be categorized into two main groups: organic and inorganic.
The following are common types of wastes found in sewage:
Organic Waste
- Biological Organic Matter: Including proteins, carbohydrates, fats, etc., from human, animal and plant excreta and waste.
- Suspended Particles: Solid particles in sewage, such as sludge, suspended matter, etc.
- Organic Acids: Including acetic acid, propionic acid, etc., are decomposition products of organic matter.
- Organic Dissolved Matter: Including various organic compounds, such as drug residues, chemicals, etc.
Inorganic Waste
- Inorganic Salts: E.g., sulfates, chlorides, nitrates, etc.
- Metal Ions: Including iron, manganese, copper, lead, etc., from industrial wastewater and pipe corrosion.
- Suspended Solids: Inorganic particles, such as minerals, sediment, dust, etc.
- Inorganic Acids Aand Bases: Including sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, etc.
Sewage may also contain a variety of hazardous substances such as heavy metals, organic pollutants, pharmaceutical residues, chemicals, and so on. These wastes can have adverse effects on the environment and health and therefore need to be removed or reduced in concentration by a suitable sewage treatment process.
What is the difference between ETP, STP and WTP?
- Effluent Treatment Plant: ETP is a facility used to treat industrial wastewater (discharged substances). Industrial wastewater can contain a variety of chemicals, pollutants, and hazardous substances that need to be properly treated to meet discharge standards in order to minimize the impact on the environment.
- Sewage Treatment Plant: STP is a facility used to treat domestic sewage and wastewater. Domestic sewage consists of wastewater from domestic, commercial, and social activities that undergoes physical, chemical, and biological treatment to convert the wastewater into environmentally friendly water for discharge or reuse.
- Water Treatment Plant: WTP is used to treat natural water sources such as groundwater, rivers and lakes in order to make them suitable for human consumption and industrial use.The treatment process in WTP consists mainly of the removal of suspended particles, impurities, chemicals, microbes and bacteria to ensure that the water quality meets the standards for drinking water and the requirements for industrial use.
ETPs are used to treat industrial wastewater, STPs are used to treat domestic wastewater, and WTPs are used to treat natural water sources for both drinking water and industrial water needs. Each type of treatment plants has its own specific treatment process and objectives to ensure the sustainable use of water resources and environmental protection.
Stp Water Composition
| Ingredient | Containing All |
| Biological organic matter | Proteins, carbohydrates, fats |
| Suspension | Sludge, particulate matter, suspended particles |
| Organic acids | Acetic acid, propionic acid, etc |
| Organic dissolved matter | Drug residues, chemicals, etc |
| Inorganic salts | Sulfates, chlorides, nitrates, etc |
| Metal ions | Iron, manganese, copper, lead, etc |
| Suspended solids | Minerals, sediment, dust, etc |
| Inorganic acids and bases | Sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, etc |
| Harmful substances | Heavy metals, organic pollutants, drug residues, chemicals, etc |
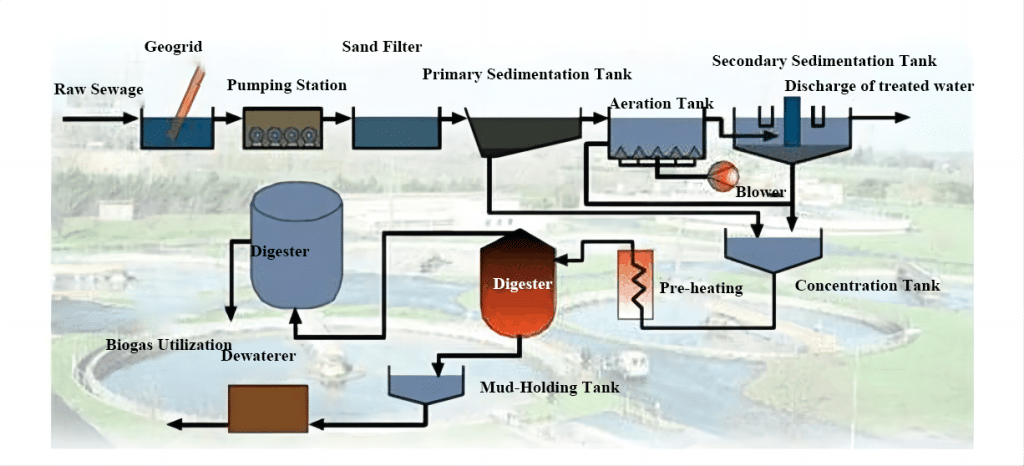
STP Treatment Process Flow
Wastewater treatment plants take wastewater through several stages of treatment. After initial filtration, wastewater treatment is divided into three main stages (primary, secondary and tertiary).
Pretreatment
Raw sewage first enters a pretreatment unit, which may include equipment such as screens, sand settling tanks, and other equipment used to remove large particles In a wastewater treatment plant, the wastewater first passes through a coarse screen in a kuosi, which removes large solids and matter and suspended matter. It then goes on to use fine screen to remove particles from the wastewater.


Primary Treatment
Wastewater enters a primary settling tank and is allowed to remain slowly to allow solids to settle to the bottom of the tank, then the water is released leaving behind a sludge/slurry that forms a substance called sludge, which reduces the suspended matter in the wastewater. Primary treatment results in the separation of solids and liquids to settle and form a wastewater that floats on top of the sludge, and the wastewater after primary treatment contains 45-50% unstable organic matter.
Biological Treatment
The conversion of organic matter in wastewater to a stabilized form through biological activity that produces secondary sedimentation. Common methods include trickling filters, aerobic digestion, anaerobic eastewater treatment and activated sludge.
- A trickling filter consists of a closed tank with a brick bed and a microbial layer. Wastewater enters the tank through an inlet and drips onto the bed through a spray nozzle. The microbial activity oxidizes the organic matter in the wastewater, which removes fine solids and creates a sludge and a wastewater with fewer organic solids.
- The activated sludge method involves adding a mixture of active microorganisms to the wastewater, followed by aeration and mixing. The main function of the aeration tank is to provide sufficient oxygen to the biological sludge to promote the decomposition and oxidation of organic matter in the effluent by the microorganisms, thus enabling biological treatment of wastewater. Aerobic conditions and microbial action oxidize the organic solids, resulting in coagulation, flocculation and settling of the solids.
Secondary Treatment
Wastewater may still contain residual pollutants after biological treatment. Further secondary treatment may include processes such as sedimentation, filtration and oxidation to further reduce pollutant concentrations.
Tertiary Treatment
Wastewater is considered clean after secondary treatment, but tertiary treatment restores it to a higher quality for discharge in protected waters, not only by removing organics through microfiltration, ion exchange, and activated carbon adsorption, but also by disinfection, which kills potential pathogens. Ozone generator can fulfill that need.
Areas Of Application For STP Water
- Sewage Treatment Plant
- Environmental Protection
- Agricultural Irrigation
- Industrial Water
- Urban Landscape Water Bodies
- Resource Recovery
Sludge From Primary And Secondary Sedimentation
Sewage sludge is digested in tanks, releasing combustible gases: methane (CH 4 ) and carbon dioxide (CO 2 ); which can be used as fuel. The digested sludge can be disposed of by sludge Incinerationor used as fertilizer.
Summary
Restoration of sewage/wastewater to the required quality and safe discharge is the most critical role of a wastewater treatment plant. Without adequate treatment, the effluent will seep into the environment and pollute the ecosystem.KUOSI is a leading manufacturer in the water treatment industry and our wide range of product lines include filter presses, screw presses, paddle dryers, dissolved air flotation machines, roots blowers, sodium hypochlorite generators, dosing system. We have a professional technical team, please feel free to contact us for a comprehensive solution to your water treatment needs.
